您想继续阅读英文文章还
是切换到中文?
是切换到中文?

THINK ALUMINIUM THINK AL CIRCLE

ASI is committed to driving the aluminium sector towards a 1.5°C-aligned future. ASI Performance Standard V3 (2022) plays a critical role in this effort, requiring transparent disclosure of science-based targets and tracking of performance by ASI Entities across the whole aluminium value chain.
Since its launch, ASI’s Certification Program has played an important role in driving responsible practices across the aluminium industry through transparent standards and credible assurance. With primary aluminium production responsible for the majority of the sector’s Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, setting and aligning GHG emissions reduction targets (GHG targets) is essential.
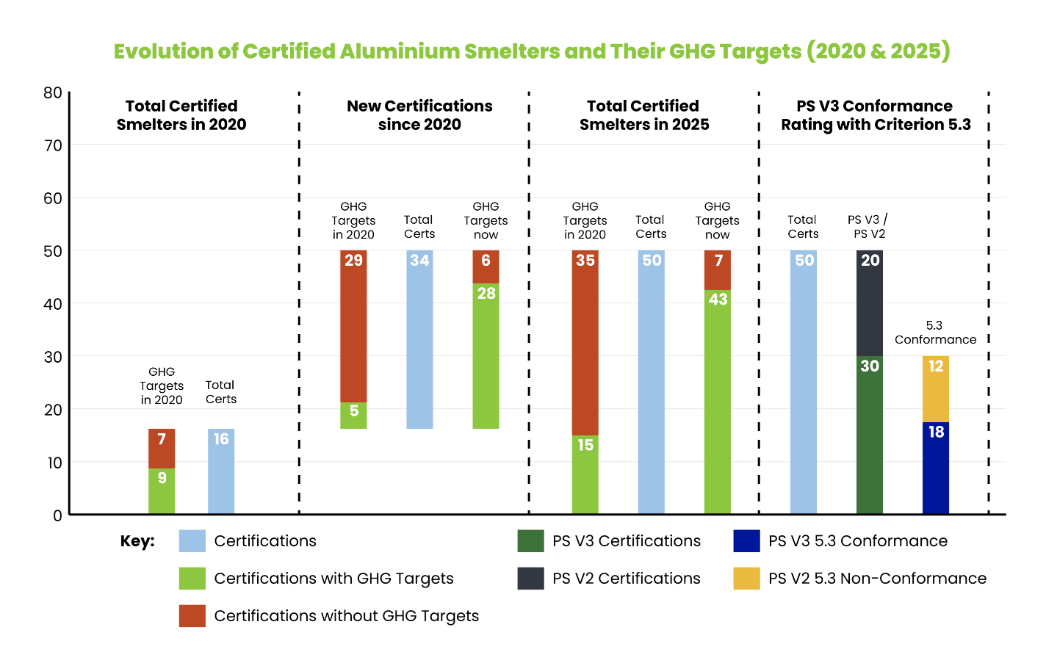
To assess how the primary industry is progressing on its GHG emissions reduction journey, we reviewed the 50 currently certified smelters and their targets. The chart below shows this evolution.
In 2020, only 16 smelters were ASI PS certified, and just 9 of them had set GHG targets (based on ASI PS V2; criterion 5.2 conformance rating).
Since then, a further 34 smelters have been certified; of this group, less than 15 per cent had GHG targets in 2020. In 2025, over 80 per cent will have GHG targets. This is a signal of how ASI Certification is attracting companies working towards a reduced GHG emissions future, as well as encouraging industry-wide climate action.
However, it’s important to note that GHG targets can vary widely in scope and ambition. Some are aligned with 1.5°C pathways, others with 2.0°C, and some are more general without a clear alignment to science-based trajectories.
The most ambitious targets are those aligned with the 1.5°C scenario (last section of the chart), as required under criterion 5.3 of the ASI Performance Standard V3. Out of currently certified smelters, only 60 per cent are certified with PS V3 (the rest have active PS V2 certificates, with future transition to PS V3). Out of the total 50 smelters, only 36 per cent (18 smelters) have targets aligned with 1.5°C pathways reflected in the conformance with criterion 5.3. There are several smelters which have non-conformance under this criterion, as their GHG targets and pathways are aligned with 2°C instead. For those smelters and those which still need to transition to PS V3, this is a significant opportunity for change. Therefore, supporting progress towards a sectoral change, as ASI Performance Standard Certifications already cover nearly 40 per cent of global primary aluminium production by volume.
With this, the ASI Performance Standard not only increases transparency through publicly disclosing data on GHG emissions and targets, but also raises the bar for the industry in setting the targets. Read more on the current ASI Standard revision here.
To further accelerate this progress, ASI has developed a 1.5°C aligned GHG Pathways Method and accompanying Calculation Tool to support Entities in setting science-aligned targets across the aluminium value chain.
Note: This article has been issued by ASI and has been published by AL Circle with its original information without any modifications or edits to the core subject/data.
Responses








