

Meeting the world’s growing energy needs while tackling environmental challenges has made renewable energy technologies more essential than ever. Among these, solar air heating systems (SAHs) and solar air collectors are emerging as a popular choice for their simplicity, scalability, and eco-friendly nature.

Solar air heating systems harness solar energy to heat air, which is then used for space heating and other applications. These systems typically include solar collectors, ductwork, and, in some cases, fans to circulate the air. As a renewable energy technology, they help reduce dependence on conventional heating methods and lower energy costs.
Recent research highlights how the smart integration of aluminium and innovative materials can redefine SAH performance, marrying waste recycling with renewable energy generation to deliver impressive efficiency gains.
In earlier studies, aluminium cans were repurposed as turbulators in a double-pass SAH to increase turbulence in airflow channels. This resulted in enhanced heat transfer, improving thermal efficiency by 30 per cent in staggered arrangements and 26 per cent in in-line configurations. Aluminium’s contribution extended further when researchers used aluminium chips as thermal energy storage media. This design achieved an 84 per cent thermal efficiency, outperforming traditional materials like mild steel and pebbles. Such success stems from aluminium’s lightweight, corrosion-resistant nature and exceptional thermal conductivity. Additionally, studies employing aluminium fins and graphene-coated aluminium ducts reported similar leaps in thermal and exergy efficiencies, solidifying aluminium’s role as an enabler in solar thermal technologies.
Brewing energy from tea dust
Taking this innovation a step further, a new study has combined agricultural waste and aluminium to create a cutting-edge solar air collector (SAC). Now, what is a SAC?
A solar air collector (SAC) is a key part of a solar air heating system (SAH). It is a type of solar collector specifically designed to heat air. In a solar air heating system, the SAC works alongside other components such as ductwork and, in some cases, a fan to circulate the heated air. Together, these elements provide warm air for space heating or other applications.
Here, activated carbon nanoparticles (ACNPs) derived from discarded tea dust was used to coat the absorber plate. When tested at varying air flow rates (0.6, 1.2, and 1.8 kg/min), the ACNP-coated SAC achieved:
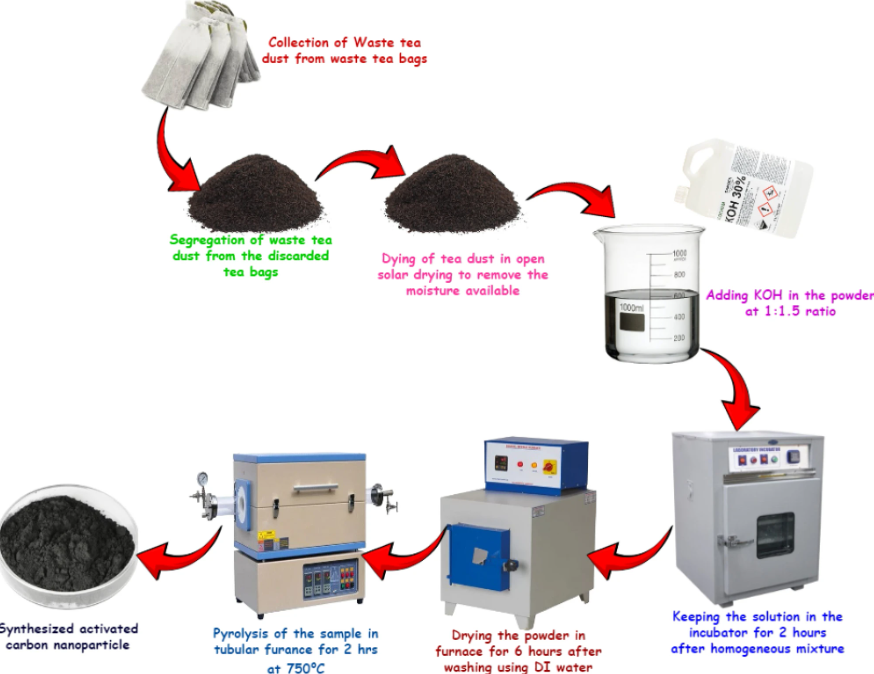
Aluminium again played a pivotal role - the SAC was insulated with aluminium foam, minimising heat loss, while aluminium’s high thermal conductivity and recyclability enhanced overall system performance and sustainability. These results highlight the dual environmental benefits of reducing agricultural waste and improving renewable energy systems. While the ACNP coating grabs the spotlight, aluminium plays a crucial supporting role in the system’s success.
Rethinking renewable energy design
This progression from structural optimisations using aluminium cans, fins, and chips to material science innovations like ACNP coatings demonstrates how aluminium remains indispensable in modern renewable energy design. Its ability to combine structural integrity, thermal performance, and recyclability aligns perfectly with circular economy goals, making it a critical component in next-generation solar technologies.
In essence, aluminium serves as the common thread uniting diverse innovations, whether as a turbulator, energy storage medium, advanced coatings base, or thermal insulation, it continues to drive breakthroughs that make solar air heating systems more efficient, eco-friendly, and economically viable. These synergistic approaches, recycling waste into high-value materials and leveraging aluminium’s unique properties, offer a blueprint for a greener, more resilient energy future.
As energy demands surge and environmental concerns intensify, such breakthroughs offer a roadmap for cleaner, more efficient technologies. The synergy between waste-derived nanomaterials and aluminium not only enhances performance but also makes renewable energy systems more accessible and sustainable. This pioneering solar air collector is a testament to how small material changes can yield big environmental and economic rewards, paving the way for a greener and more resilient energy future.
Also Read: Sohar Aluminium advances sustainability with focus on efficiency and decarbonisation
Image Source: nature.com
Responses








