

Climate change around the world is causing great catastrophes, with no continent left untouched. The heatwaves, droughts, typhoons, and hurricanes are causing mass destruction around the world with disasters such as the heatwave in the UK, the West’s water crisis, hurricane Ian in the US, and many more.

Mohan Agarwal, MD, CMR Green Technologies Ltd
Countries around the globe are now shifting their focus on sustainability with real and measurable actions. The focus is now on developing sustainable products and services and supply chain practices to increase revenue, satisfy investors and regulators, and improve their reputation. Countries as well as companies are allocating funds to addressing environmental issues. McKinsey and Company recently said that India can increase green investments up to USD 12.1 trillion by 2050 and reap many benefits.
Among the COP meetings, the game-changing COP 3 – Kyoto Protocol 1997 called upon 37 industrialised economies to bring down Green House Gas (GHG) emissions. The deliberations ended with assurances, commitments and promise to adopt graded methods to combat global warming. After the Kyoto protocol, the next tectonic commitment was made at COP 21 meeting in Paris in 2015 followed by the recent COP 26 and COP 27. COP 26 in 2021 acted as a milestone with substantial commitments from around the world along with India’s 5-point pledge or Panchamrit. Taking a step further, at COP27, India submitted its Long-Term Low Emission Development Strategy (LT LEDS) to UNFCCC. These conferences have time and again stressed the need for businesses to create action plans to mitigate human influence on the climate and nature.
Expectations are growing for businesses to play a proactive role in driving efforts to secure a sustainable and inclusive future for the next generation. A growing coalition of countries, cities, businesses and other institutions are pledging to get to net-zero emissions. More than 70 countries, including the biggest polluters – China, the United States, and the European Union – have set a net-zero target, covering about 76% of global emissions. And more than 1000 cities, over 1000 educational institutions, and over 400 financial institutions have joined the Race to Zero, pledging to take rigorous, immediate action to halve global emissions by 2030.
Aluminium is one of the most sustainable materials in the world and is also highly recyclable. Recycled Aluminium meets every criterion of the 6R circular economy- reduce, reuse, recycle, recover, redesign and re-manufacture. Moreover, recycling Aluminium scrap requires only 5% of the energy used to produce the same amount of primary aluminium. With these advantages, Aluminium production through the primary route is being increasingly substituted with secondary production.
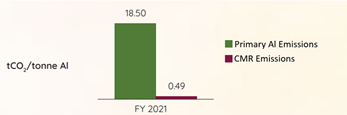
The GHG Emissions from the Secondary Production of Aluminium are substantially less concerning than those of the Primary Production of Aluminium, as is reflected in the graph below:
GHG Comparison of CMR vs Companies using Raw Aluminium:
As an organization, CMR is aligned with sustainability principles as they are deeply ingrained in the organizational DNA. It is a matter of great satisfaction that the core of our business, i.e., recycling of metals, has many significant environmental benefits as sustainability is embedded in the product itself and it promotes a circular economy. Leveraging on the multiple environmental advantages which our business has to offer, we have well-planned initiatives to improve our performance in key environmental areas like emissions, solid-waste generation, hazardous waste generation, and Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions to reduce the overall impact on our natural resources and environment. Also, we have created a culture that rewards talent and continuous learning for the organization to be future-ready and to meet the challenges posed by ever-changing market realities. We promote employee diversity and nearly 50% of our workforce is women.
At CMR, we are establishing a long-term sustainability strategy within a robust Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) framework. Our Sustainability Report adheres to the reporting principles of GRI Standards addressing principles of Accountability i.e., materiality, stakeholder inclusiveness, sustainability context and completeness.
We believe that stakeholder engagement and identifying material issues are key to success for sustainable development. The expectations and the concerns of stakeholders and the extent to which the relevant issues are addressed play a vital role in influencing the sustainable growth of an organization. To identify the Material Topics, we obtained critical inputs during the engagement and consultation process with our stakeholders. The same is reflected below:

The above 12 essential Material Topics have been aligned with the UN SDGs
CMR Group is a very conscious green organization focusing on the recycling of metal and has adopted world standards of emissions and zero discharge company policy. The air quality from our baghouses not only meets most of the requirements of Japanese and European standards but also is far below the accepted Indian standards for ambient air quality emissions.
We as an organization have adopted various equipment and systems to control our SOx, NOx and PM emissions, to lower environmental damages.
For reducing NOx levels, we have used regenerative burners in our furnaces that use exhaust gases to reheat the furnace hence reducing fuel consumption and at the same time providing a much cleaner output content. A regenerative burner system generally ignites a pair of burners integrated with the heat reservoirs alternately at intervals of several tens of seconds. While one burner is burning, the exhaust gas passes through and heats the other burner’s heat reservoir to recover the energy of the exhaust gas. Then, when the other burner fires, the air for combustion in turn passes through the preheated heat reservoir to recover the exhaust gas energy which had conventionally been wasted, to provide highly efficient combustion. Alumina ball present in the burner reservoir, help to absorb heat which preheat the chamber air and it also absorbs harmful SOx, NOx and Carbon particle which results in the purifying exhaust gas. Table 1 provides a comparison between NOx emission as per Govt. Standard vs CMR’s Emission Data.

Table 1 – Comparison of NOx emission of Manesar unit
The output from the regenerative burners (flue gases) is then transferred to bag houses, these bag houses have hot air passed through a tube settler and the tubes get cooled from outside by fresh air purging. A settling chamber helps to drop flue gas temperature. Typically, via an induced draft blower, the flue gas is drawn into the bag house through a duct system. The flue gas then passes through the specialised bag filters & lime powder is sprayed on them, which helps in entrapping the sulphur contents & particulate matters, thus separating the SOx & particulates from the air. Over time, the dust begins to build up and form a carbon layer on the filter surface. By offline air purging in filters, carbon layers are removed, and carbon is collected into the bags. Clean air is exhausted into the atmosphere via the chimney by a blower. Table 2 provides a comparison between SOx emission and Particulate Matter as per Govt. Standard vs CMR’s Emission Data.
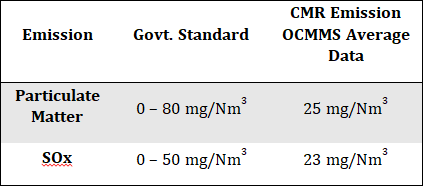
Table 2 - Comparison of PM & SOx emission of Manesar Unit
CMR was the first to start delivering ready-to-use liquid Aluminium alloy directly to customers’ production lines. CMR Group has made significant investments to introduce liquid metal supply in this industry by opening their production units near the customer facilities. This has served as an effective method for emission reduction. Liquid metal supply eliminates the entire process of ingot melting by die-caster, which would otherwise lead to wastage of fuel and loss of metal (melt loss). Around 3.6 million tonnes of CO2 saved against the production of 1.8 lac tonnes of recycled aluminium compared with manufacturing through the primary routes.
Moving with an accelerated pace, we have digitized and centralized our systems. All Plants are strategically integrated to optimize the supply chain, resulting in further reduction of Scope 3 of the GHG Protocol. Our Centralized Monitoring System implemented through the internal ERP system is used to monitor all major parameters like fuel consumption, dross generation, material movement and all major aspects of operations.
Technology Adoption:
At CMR, we always look for the best technology available worldwide and are the first to adopt it in the industry. To produce the Aluminium alloy ingots, the latest technologies are employed for sorting like dense media separators, magnetic drums, eddy current separators, colour sorters, etc. We have installed the MTS (Metal Treatment System) machine used for the effective degassing of molten aluminium which helps in improving the quality of material and reducing dross generation. We have also changed the refractory lining of ladles to special material linings, which helps in reducing the heat dissipation per minute from ladle to transport molten metal to longer distances.
To improve the overall yield percentage, we have installed a highly efficient pump furnace for the melting of scraps. Also, the Integrated Dross Screw Machine helps in the same by increasing the recovery of aluminium from dross. Further, the scrap dryer machine for preheating and reducing the moisture from the scraps helps in reducing dross generation and thus improving the metal recovery. CMR is also in process of changing its manually operated furnaces to automatic furnaces to maintain the air-fuel ratio which helps in reducing fuel consumption along with emissions.
Carbon Projects: CMR has been accredited by the UNFCCC (United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change) as an environmentally clean plant, eligible for Carbon Credits in 2015.
Since then, we have undertaken Carbon Credit Projects for our existing and upcoming Plants. Some details of existing projects are:
CDM: CMR has registered the Carbon Development Mechanism project at Bhiwadi, Rajasthan. The proposed project activity reduced the dependence on fossil fuel and avoid associated Aluminium metal loss due to oxidation during remelting of ingots, thereby, effecting an overall reduction in GHG emissions. Annual average GHG emission reduction because of the project activity is estimated to be about 8,713 tCO2 equivalent per year. The total GHG emission reduction over the entire crediting period of 10 years is estimated to be about 87,130 tCO2 equivalent with one plant project alone.
GCC: CMR has registered Global Carbon Council Project for 3 plants, for which the validation, registration and verification are ongoing.
Energy:
At CMR, our strategic commitment is to reduce specific energy consumption and increase renewable energy share across all locations. CMR laid a strong focus on optimizing energy consumption through stricter operational control and initiated several efficiency improvement actions. We give prime importance to achieving energy-saving projects. Energy-efficient heavy motors, drives, and pumps are installed at all sites while idle running of equipment is significantly reduced to curtail electricity consumption. A review of energy consumption is carried out at various levels of the organization. We continuously monitor the energy consumption across all sites in our inter-unit management review meetings.
Each tonne of aluminium is manufactured through recycling. results in a saving of 5-6 tonnes of bauxite, 1-1.5 tonnes of limestone, 20- 25 tonnes of water and~14000 kWh of energy (~90-95% of energy savings as per International Aluminium Institute). It means CMR saves approximately 2.8 Million MW of energy per annum which is equivalent to more than 50 villages’ energy consumption.
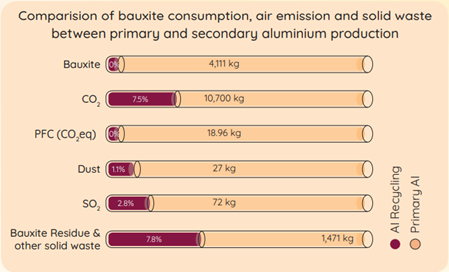
CMR promotes a circular economy through the use of low-impact practices and new resource-efficient technology. Material Circularity Index (MCI) as per the MacArthur Foundation framework for primary Aluminium production in India is around 0.22. 100% circular product has an MCI of 1 while 100% linear product has an MCI of 0.1. The MCI of our product is around 0.89 while the MCI for the global aluminium mix of primary and secondary aluminium comes to around 0.56.
As a part of our decarbonization roadmap, some significant initiatives have been planned for the near future: With respect to Renewable Energy, CMR has an ambitious plan to install solar energy units at various locations, including Tatarpur, Bawal, Haridwar, Vanod and Pillaipakkam. In addition to this, we will be incorporating Fuel and Energy reduction measures. These will include a reduction in existing fuels i.e., Low Sulphur Heavy Stock & Fuel Oil; reduction of HSD and LDO; Conversion to Piped Natural Gas from heavy fuels; and replacements of diesel forklifts by electrical forklifts across our operations. These will significantly reduce fuel consumption and consequently GHG emissions.
On the one hand, we try to prevent uncontrolled energy use and associated emissions. While on the other hand, we expect increased use of recycled aluminium in the automobile, railway traction, packaging, and construction sectors as a preventive measure against climate change. Moreover, we are also committed to achieving net zero emissions by 2050.
The sustainability strategy is an integral part of CMR's business strategy. We leverage business opportunities, minimize risk and seek to respond to social and environmental challenges such as scarcity of resources and climate change at an early stage. With the growing demand for Aluminium worldwide and the increased need to meet environmental benchmarks, Green Aluminium is gaining momentum. We are also converting our Aluminium to Green Aluminium with the best possible practices, such as increasing renewable energy sources, investing in cutting-edge technologies and accelerating our decarbonization efforts.
We are sure that CMR will reach greater heights in our journey of Sustainable Development in the coming years through our well-thought-out plans and its implementation.
Responses








