

The International Aluminium Institute (IAI) has revealed new data on the aluminium industry’s achievements in diminishing energy efficiency in the industry’s constant sustainability mission. The data release accords with a series of announcements in the lead up to COP26 in Glasgow.
The aluminium industry’s energy usage accounts for over two-thirds of global greenhouse gas emissions. The results from the 2020 Global Energy Survey conducted by the IAI deliver evidence of an industry customising pathways to manage the problem.
The annual survey, which had a 90% response rate across the global industry, demonstrates the use of sustainable production processes and competently managed to reduce its impact on the environment.
Linlin Wu, IAI’s Manager – Statistical Analysis said: “Our industry has kept the momentum in energy efficiency improvement during the pandemic, with average energy intensity of both smelting and refining improving by about 0.5% compared to the previous year. This is a testament to the industry’s commitment to continuous improvement in emissions reduction. It also demonstrates our commitment to providing transparency of footprint across the entire aluminium value chain”.
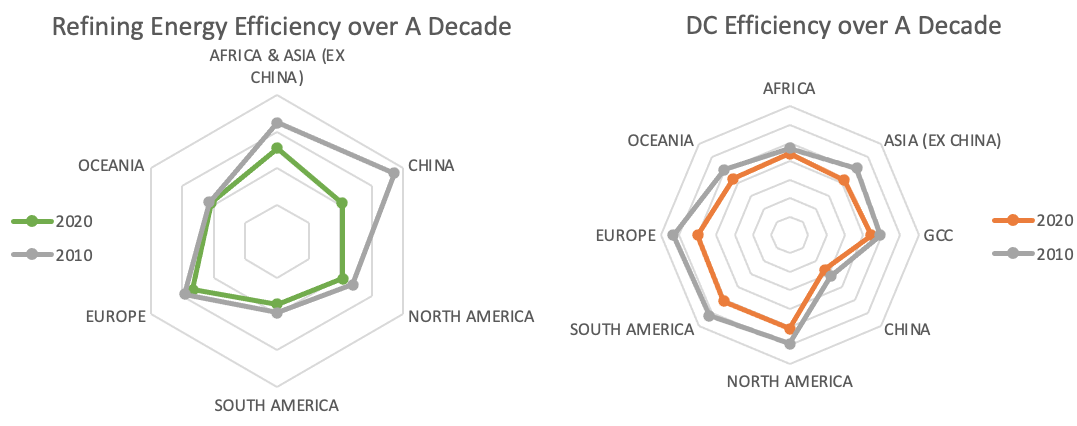
Data from the survey revealed that over the past decade, global production of primary aluminium and metallurgical alumina (aluminium oxide) has increased by 54% and 50%, respectively. Despite this vast production increase, refining energy intensity reduced by 25% and electrolysis energy intensity decreased by 4%. The impact of this 10-year energy saving is the equivalent of 3.2 TeraWatt – or the annual energy consumption of a country like Jamaica.
Figures from the industry’s six regions indicate that China significantly improved its energy efficiency in refining, while smelting improvements were consistent across eight regions.
Even during the Covid-19 pandemic, the aluminium industry maintained its energy efficiency improvement with reductions in both smelting and refining energy intensity of 0.5% compared to 2019.
Aside from improving energy efficiency, the sector is also adopting greater use of renewable energy in the entire power mix as it strives to lower its carbon footprint.
Over the course of 2020, renewable energy grew by 1% - with all regions bar Asia (outside China) showing an increase.
“This 2020 Global Energy Survey data is part of overarching data analysis which underpins our overall sustainability work across the spectrum. For example, analysis of energy data over time informs our body of work including our recently published Aluminium Sector Greenhouse Gas Pathways to 2050,” said Ms Wu.
The aluminium industry is amongst the most proactive in the materials and metals sector at seeking environmental solutions.
Data last year from the IAI also revealed that more than 30 million tonnes of aluminium scrap are recycled globally, ensuring its status as one of the most recycled materials on the planet.
Aluminium is central to a sustainable future because of its unique combination of properties, including lightness, strength, durability, and recyclability.
Responses








